Time for angles
04 March, 2019Readtime: 3 mins
I was once asked in an interview to calculate the angle between the minute and hour hands on a clock for the time 16:34. This was tricky to do in my head but possible given 2 simple facts.
- The minute hand moves 6 degrees for every minute, since we have 360 degrees for one revolution and 60 minutes in an hour, hence 360/60 = 6 degrees/minute.
- The second is that the hour hand moves 30 degrees for every hour, again 360 degrees and now 12 hours in one revolution, hence 360/12 = 30 degrees/hour.
However, the hour hand also moves 0.5 degrees for every minute, since the hour hand covers 30 degrees in 60 minutes. Well knowing this we can then simply do 34 X 6 degrees = 204 degrees for the minute hand and (4 X 30 degrees) + (34 X 0.5 degrees) = 137 degrees for the hour hand. Thus, we have (taking the small angle) a difference of 67 degrees, or 1.17 radians if you prefer.
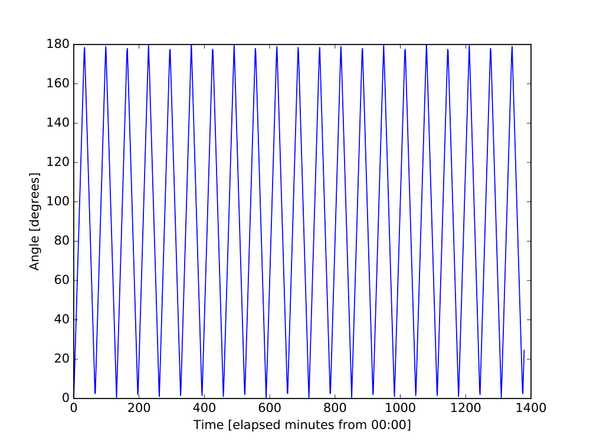
The obvious follow up question was then - What is the time when the hands next cross? Well to answer this I have plotted the angle as a function of time (in minutes).
We can see from printing out the times at which the angle is a minimum gives us 17:27 (to the nearest minute). The full list of cross over times are:
| Time(HH:MM) | Angle (Deg) |
|---|---|
| 00:00 | 0.0 |
| 01:05 | 2.5 |
| 02:11 | 0.5 |
| 03:16 | 2.0 |
| 04:22 | 1.0 |
| 05:27 | 1.5 |
| 06:33 | 1.5 |
| 07:38 | 1.0 |
| 08:44 | 2.0 |
| 09:49 | 0.5 |
| 10:55 | 2.5 |
| 12:00 | 0.0 |
| 13:05 | 2.5 |
| 14:11 | 0.5 |
| 15:16 | 2.0 |
| 16:22 | 1.0 |
| 17:27 | 1.5 |
| 18:33 | 1.5 |
| 19:38 | 1.0 |
| 20:44 | 2.0 |
| 21:49 | 0.5 |
| 22:55 | 2.5 |
Alas, I didn’t get the job in the end, but for anybody who has this question, or is simply curious next time they are staring at the clock, the vanilla Python script (version 3 compatible) below should help.
import math
#constants
twoPi = 2.0*math.pi
maxDegree = 360.0
secondsInHour = 60
minutesInHour = secondsInHour
hoursInDay = 24
maxHour = math.ceil(hoursInDay/2)class Clock():
def __init__(self, hour, minute, radians):
self.hour = hour
self.minute = minute
self.radians = radians
self.factor = twoPi
if not radians:
self.factor = maxDegree
self.validateTime()
def validateTime(self):
if self.hour > hoursInDay - 1 or self.hour < 0:
raise ValueError('Time must be valid - check hours')
if self.minute > minutesInHour - 1 or self.minute < 0:
raise ValueError('Time must be valid - check minutes')
def __str__(self):
return "Standard time is: {}, Time in minutes : {}, , Angle: {}".format(
self.getTimeStandardAsString(),
self.getTimeInMinutes(),
self.computeAngle())
def getTimeStandardAsString(self):
timeInMinutes = self.getTimeInMinutes()
hours = str(math.floor(timeInMinutes/minutesInHour))
mins = str(timeInMinutes % minutesInHour)
if len(hours) == 1:
hours = "0" + hours
if len(mins) == 1:
mins = "0" + mins
return hours + ":" + mins
def getTimeInMinutes(self):
return self.hour*minutesInHour + self.minute
# every minute moves the minute hand by 6 degrees
def computeMinuteAngle(self):
return self.minute*self.factor/minutesInHour
# every hour moves the hour hand by 30 degrees and each minute moves the hour hand by 0.5 degrees
def computeHourAngle(self):
# convert to non 24 hour (between 0 and 12 only)
simpleTimeHour = self.hour
if simpleTimeHour > maxHour:
simpleTimeHour = simpleTimeHour - maxHour
return (simpleTimeHour*self.factor + self.computeMinuteAngle())/maxHour
def computeSmallAngle(self):
minuteAngle = self.computeMinuteAngle()
hourAngle = self.computeHourAngle()
angle = abs(hourAngle - minuteAngle)
return min(angle, abs(self.factor - angle))
def computeLargeAngle(self):
return self.factor - self.computeSmallAngle()
def computeAngle(self):
return self.computeSmallAngle()If we then plug in the desired time, 16:34, behold we get 67 deg.
clock = Clock(16,34, False)
print(clock)
Written by Thomas Stainer who likes to develop software for applications mainly in maths and physics, but also to solve everyday problems. Check out my GitHub page here.